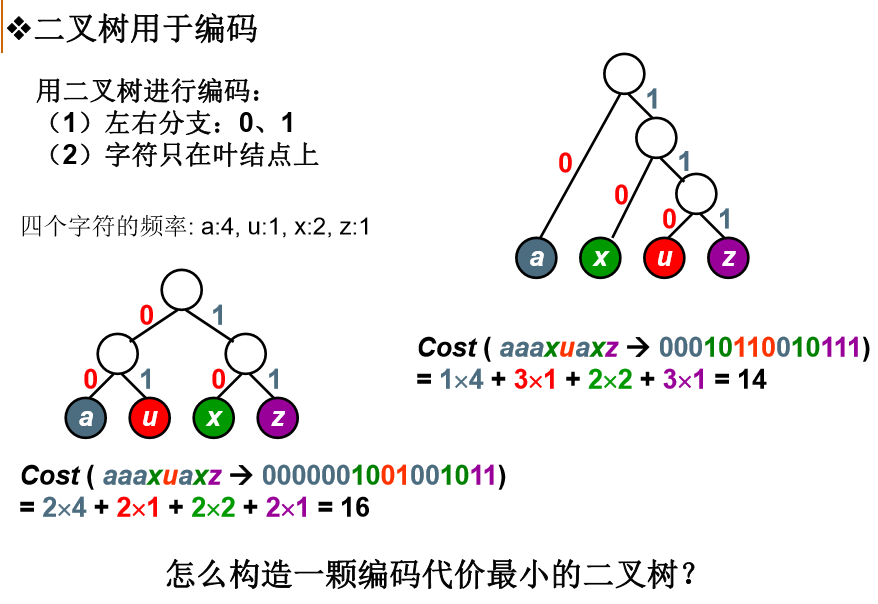
哈夫曼树
哈夫曼树
0x00 什么是哈夫曼树
哈夫曼树是为了解决叶节点带权路径和最短问题
考虑下面这个关于成绩转换的例子:
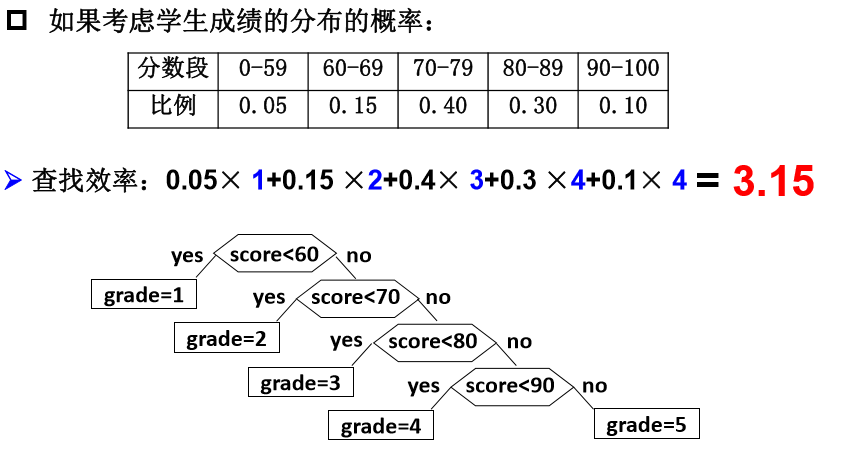

我们将上面的效率称为带权路径长度(WPL):设二叉树有n个叶子节点,每个叶子节点带有权值Wk,从根节点到每个叶子节点的长度位Lk,则每个叶子节点的带权路径长度之和就是WPL
而哈夫曼树huffman (又称最优二叉树):WPL最小的二叉树
0x01 哈夫曼树的构造
哈夫曼树的构造是很简单,很容易实现的,每次都把权值最小的两棵二叉树合并。
例如权值分别为1,2,3,4,5,其构造过程如下:

代码实现如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define maxsize 1000
#define minnum -1000
typedef struct tnode* hmnode;
struct tnode{
int weight;
hmnode left;
hmnode right;
};
typedef struct heap* minheap;
struct heap{
hmnode* data;
int capacity;
int size;
};
hmnode createnode(int w){
hmnode ret=(hmnode)malloc(sizeof(struct tnode));
ret->weight=w;
ret->left=NULL;
ret->right=NULL;
return ret;
}
minheap createheap(){
minheap ret=(minheap)malloc(sizeof(struct heap));
ret->capacity=maxsize;
ret->size=0;
ret->data=(hmnode*)malloc(sizeof(hmnode)*(ret->capacity+1));
ret->data[0]=createnode(minnum);
return ret;
}
minheap insert(minheap h,hmnode x){
if(h->size==h->capacity){
printf("堆满!");
}else{
h->data[++h->size]=x;
int child=h->size;
int parent=child/2;
while(h->data[child]->weight<h->data[parent]->weight){
hmnode temp=h->data[child];
h->data[child]=h->data[parent];
h->data[parent]=temp;
child=parent;
parent=child/2;
}
}
return h;
}
hmnode del(minheap h){
hmnode ret=NULL;
if(h->size){
ret=h->data[1];
h->data[1]=h->data[h->size--];
int parent=1;
int child=parent*2;
for(;child<=h->size;){
int min=h->data[child]->weight;
int pos=child;//默认左儿子最小;
if(child+1<=h->size&&h->data[child+1]->weight<h->data[child]->weight){
min=h->data[child+1]->weight;
pos=child+1;
}
if(h->data[parent]->weight>min){
hmnode temp=h->data[parent];
h->data[parent]=h->data[pos];
h->data[pos]=temp;
parent=pos;
child=2*parent;
}
}
}else{
printf("堆空!");
}
return ret;
}
hmnode createtree(int * list,int size){
minheap h=createheap();
int i;
for(i=0;i<size;i++){
insert(h,createnode(list[i]));
}
while(h->size>1){
hmnode a=del(h);
hmnode b=del(h);
hmnode c=createnode(a->weight+b->weight);
c->left=a;
c->right=b;
insert(h,c);
}
return h->data[1];
}
void traversal(hmnode t){
if(t){
printf("(%d)\n",t->weight);
traversal(t->left);
traversal(t->right);
}
}
int main(){
int a[]={1,2,3,4,5};
hmnode t=createtree(a,5);
traversal(t);
return 0;
}
以上代码测试通过
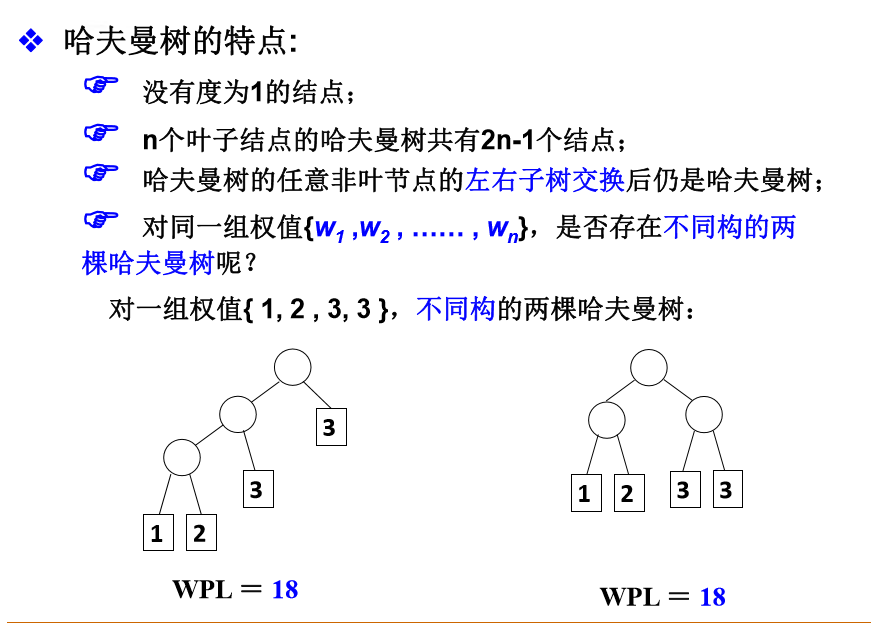
0x02 哈夫曼树的特点
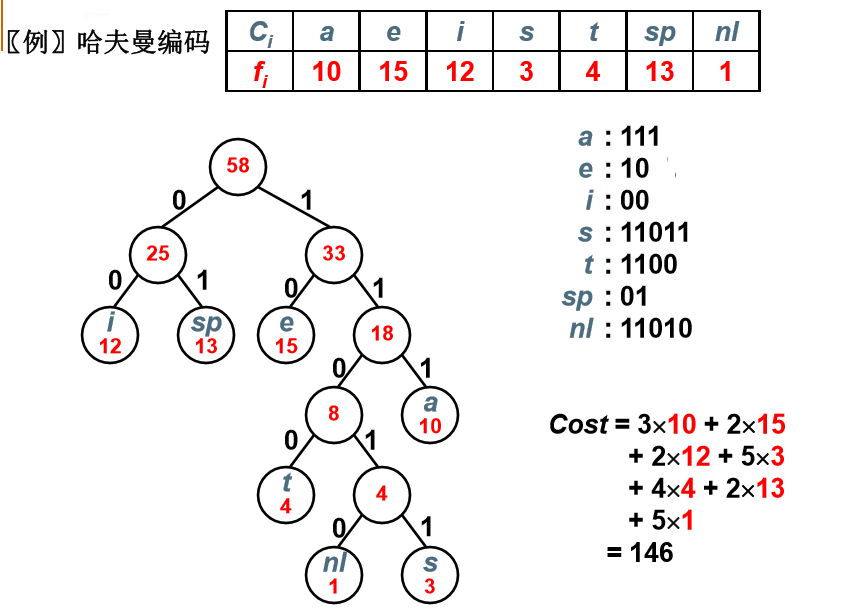
0x03 哈夫曼编码
一段给定的字符串,其每个字符的频率我们已知,如果用等长编码,则占空间较大,使用不等长编码即可,但是不等长编码会出现二义性,如10代表’A’,101代表’B’,则会出现歧义。而通过哈夫曼树,就可以产生没有二义性的不等长编码,且占用空间最小 我们在建立huffman树的时候,规定每次选两个最小的时候,较小的那个作左子树,代表编码0,另一个则编码1。这样,我们就可以遍历建成的huffman树,来获取每个字符对应的编码。